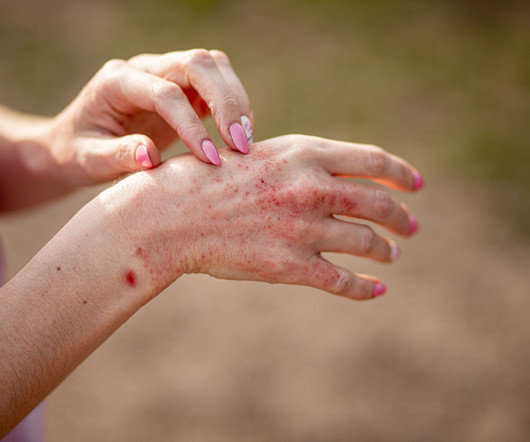
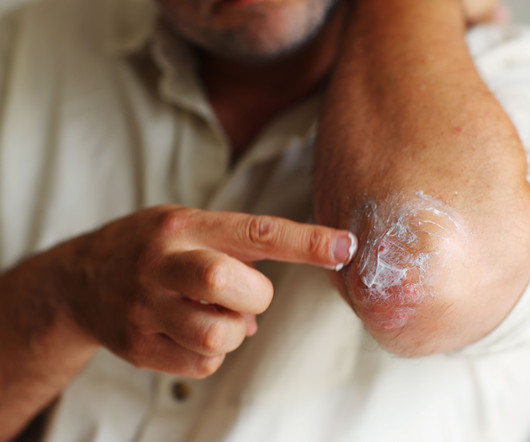
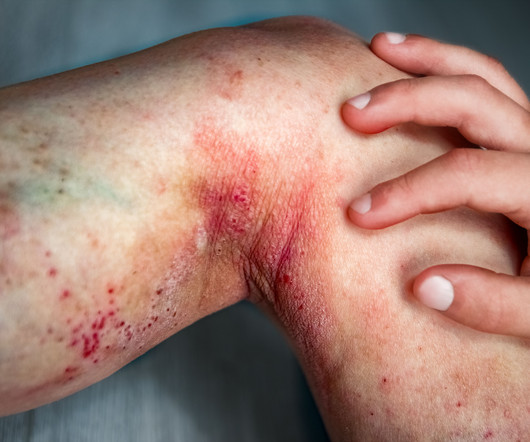
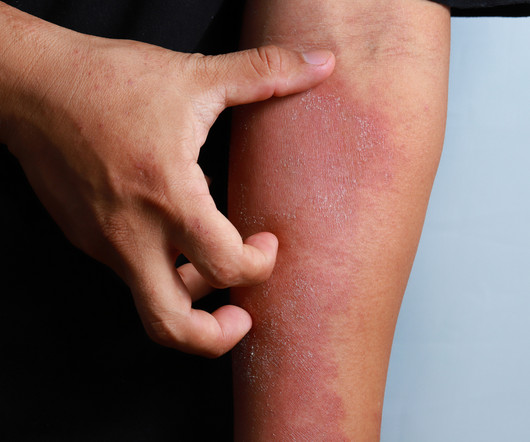
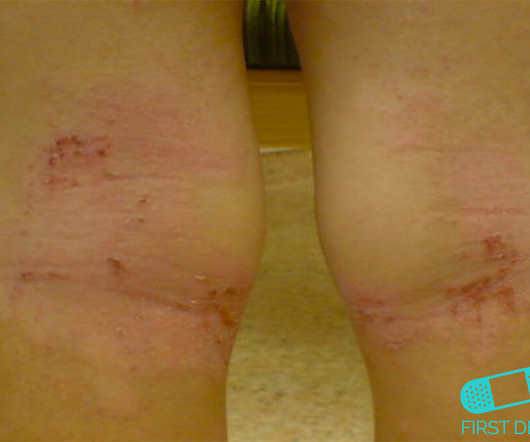
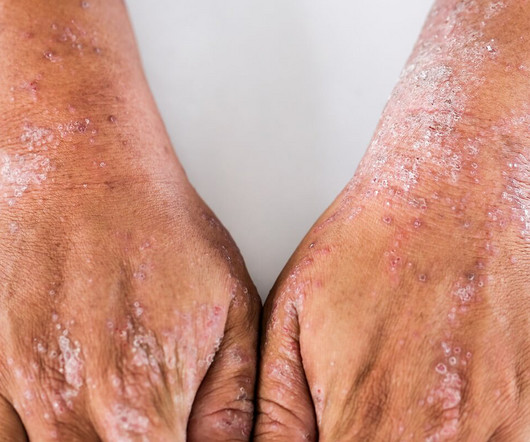
Real-World Insights: Systemic Therapies in Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis Patients
Dermatology Times
OCTOBER 3, 2023
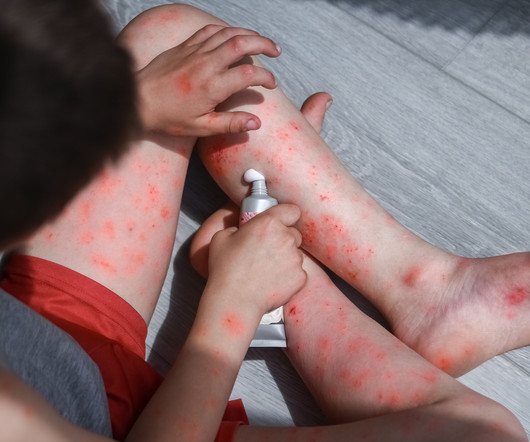
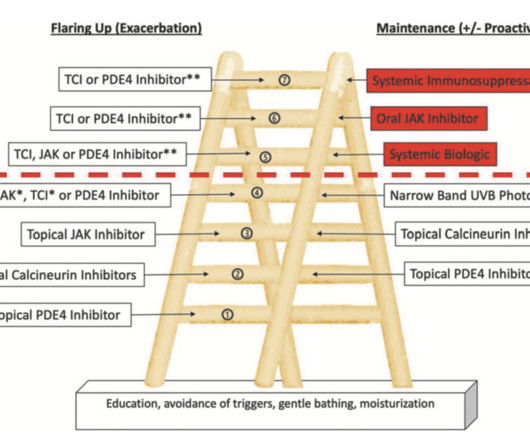
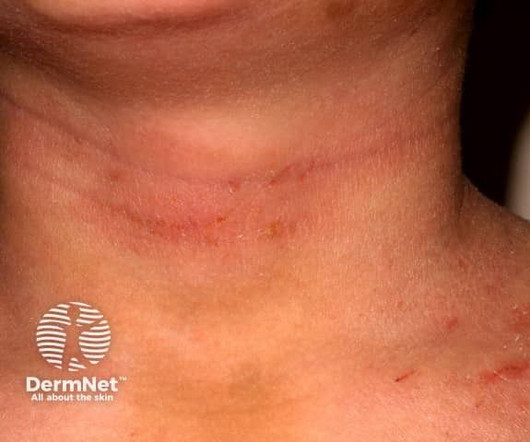
These insights highlight the crucial role of systemic therapies in the comprehensive management of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis.





































Let's personalize your content